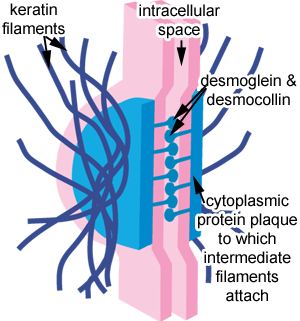
1. adhering junction:Junction where a mass of anchored proteins help adjoining cells adhere.
2. adipose tissue :A connective tissue having an abundance of fat-storing cells.
3. blood:Fluid connective tissue of water, solutes, and formed elements (blood cells, platelets). Transports substances to and from cells, helps maintain internal environment.
4. bone tissue:Of vertebrate skeleton, a tissue of osteoblast secretions hardened with minerals.
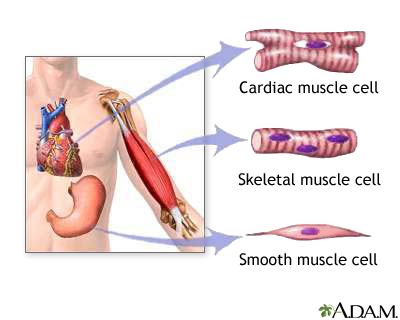
5. cardiac muscle tissue:A contractile tissue that is present only in the heart wall.
6. cartilage:Connective tissue with solid, pliable intercellular material that resists compression.
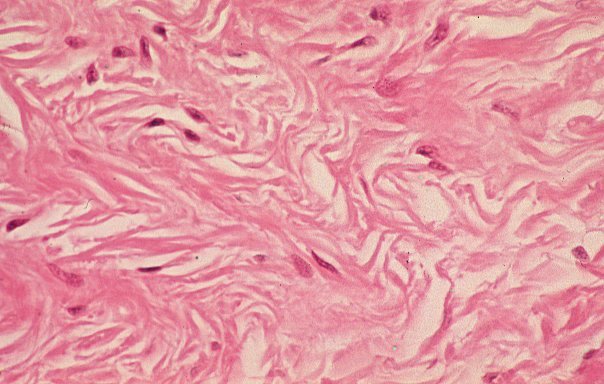
7. dense, irregular connective tissue :Animal tissue with fibroblasts, many asymmetrically positioned fibers in ground substance. In skin and some capsules around organs.
8. dense, regular connective tissue:Animal tissue with rows of fibroblasts between parallel bundles of fibers. In tendons, elastic ligaments.
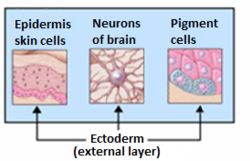
9. ectoderm:The first-formed, outermost primary tissue layer of animal embryos; gives rise to nervous system tissues and integument's outer layer.
10. endocrine gland:Ductless gland that secretes hormones, which the bloodstream distributes.
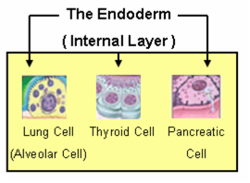
11. endoderm:Inner primary tissue layer of animal embryos; source of inner gut lining and derived organs.
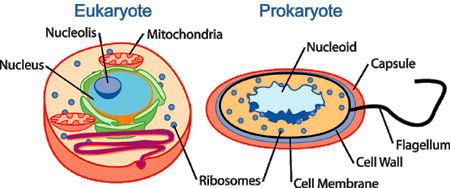
12. epithelium:Animal tissue that covers external surfaces and lines internal cavities and tubes. One surface is free and the other rests on a basement membrane.
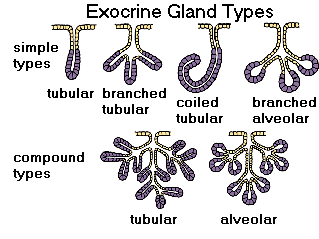
13. exocrine gland :Glandular structure that secretes products, usually through ducts or tubes, to a free epithelial surface.
14. gap junction: Cylindrical arrays of proteins in the plasma membrane that pair up as open channels for signals between adjoining cells.
15. gland cell: A cell that secretes products unrelated to their own metabolism for use elsewhere
16. homeostasis:State in which physical and chemical aspects of internal environment (blood, interstitial fluid) are being maintained within ranges suitable for cell activities.
17. internal environment: Blood + interstitial fluid.
18. loose connective tissue:Animal tissue with fibers, fibroblasts loosely arrayed in semifluid ground substance.
19. mesoderm:Primary tissue layer of all large, complex animals; gives rise to many internal organs and part of the integument.
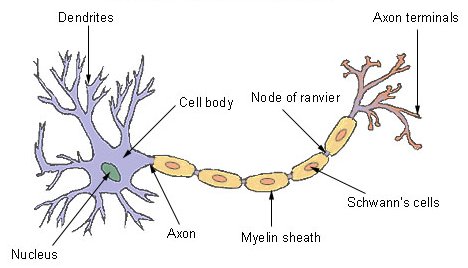
20. nervous tissue: Connective tissue composed of neurons and often neuroglia.
21. neuroglia: Collectively, cells that structurally and metabolically support neurons. They make up about half the volume of nervous tissue in vertebrates.
22. neuron:Type of nerve cell; basic communication unit in most nervous systems.
23. organ:Body structure with definite form and function that consists of more than one tissue.

24. organ system: Organs interacting chemically, physically, or both in a common task.
25. skeletal muscle tissue:Striated contractile tissue that is the functional partner of bone.
26. smooth muscle tissue:Nonstriated contractile tissue found in soft internal organs.
27. tight junction :Cell junction where strands of fibrous proteins oriented in parallel with a tissue's free surface collectively block leaks between the adjoining cells.

28. tissue: Of multicelled organisms, a group of cells and intercellular substances that function together in one or more specialized tasks.